
Historical Journal Archive database
Searchable database for medical journal abbreviations, both modern and historical, aiding researchers in accessing articles to facilitate easier navigation of medical literature through improved referencing.

Searchable database for medical journal abbreviations, both modern and historical, aiding researchers in accessing articles to facilitate easier navigation of medical literature through improved referencing.

McGinn and White first described the so-called S1Q3T3 pattern in five patients with acute cor pulmonale secondary to pulmonary embolism.

Postpartum hypopituitarism following ischaemic necrosis of the anterior pituitary gland. Pituitary necrosis occurs secondary to hypophyseal portal vessel thrombosis following significant postpartum haemorrhage, hypovolemia, and shock.

Peutz-Jeghers-syndrome: A Syndrome gastrointestinal polyposis characterized by specific melanin pigmentations of the skin and mucous membranes
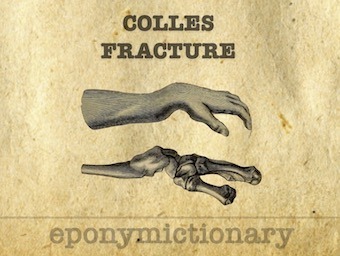
Colles fracture: Extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation of the distal fragment. Abraham Colles (1814)
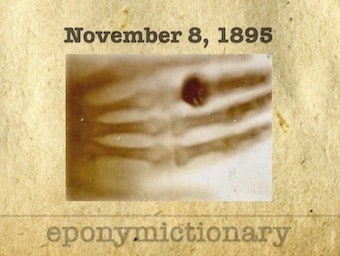
On November 8, 1895 Wilhelm Röntgen, chair of physics at Würzburg, noted an unusual phenomenon, that would change the world of medicine

Bryant’s sign: Scrotal ecchymosis associated with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) first described in 1903 by John Henry Bryant (1867-1906)
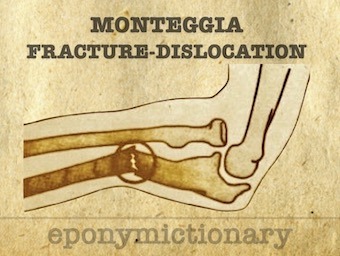
Monteggia fracture. Fracture of the proximal or middle third of the ulna with associated radial head dislocation/instability. GB Monteggia 1812

Galeazzi fracture (1934). Fracture of the distal third of the radius with associated Distal radio-ulna joint (DRUJ) disruption.

Naxos disease: a recessively inherited condition with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/ cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma, and woolly hair
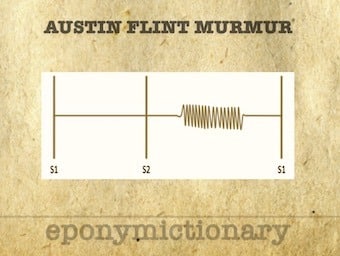
Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis

Primary thrombosis of the subclavian vein at the costoclavicular junction. The formation of an axillo-subclavian vein thrombosis results from endothelial trauma, often as a result of repetitive activity of the upper limbs.